Points3D
A 3D point cloud with positions and optional colors, radii, labels, etc.
If there are multiple instance poses, the entire point cloud will be repeated for each of the poses.
Fields fields
Required required
positions:Position3D
Recommended recommended
Optional optional
labels:Textshow_labels:ShowLabelsclass_ids:ClassIdkeypoint_ids:KeypointId
Can be shown in can-be-shown-in
- Spatial3DView
- Spatial2DView (if logged above active projection)
- DataframeView
API reference links api-reference-links
Examples examples
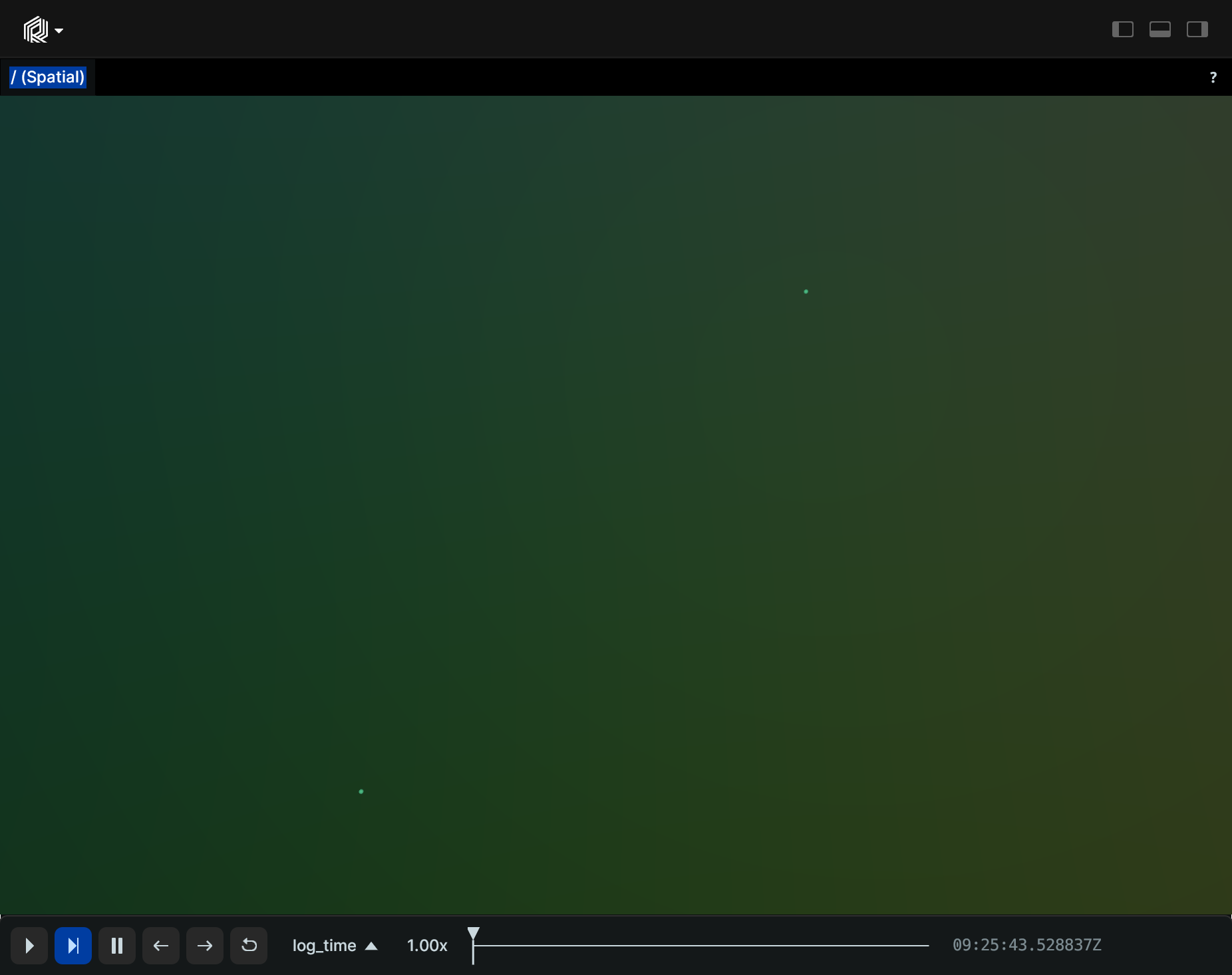
Simple 3D points simple-3d-points
"""Log some very simple points."""
import rerun as rr
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d", spawn=True)
rr.log("points", rr.Points3D([[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1]]))
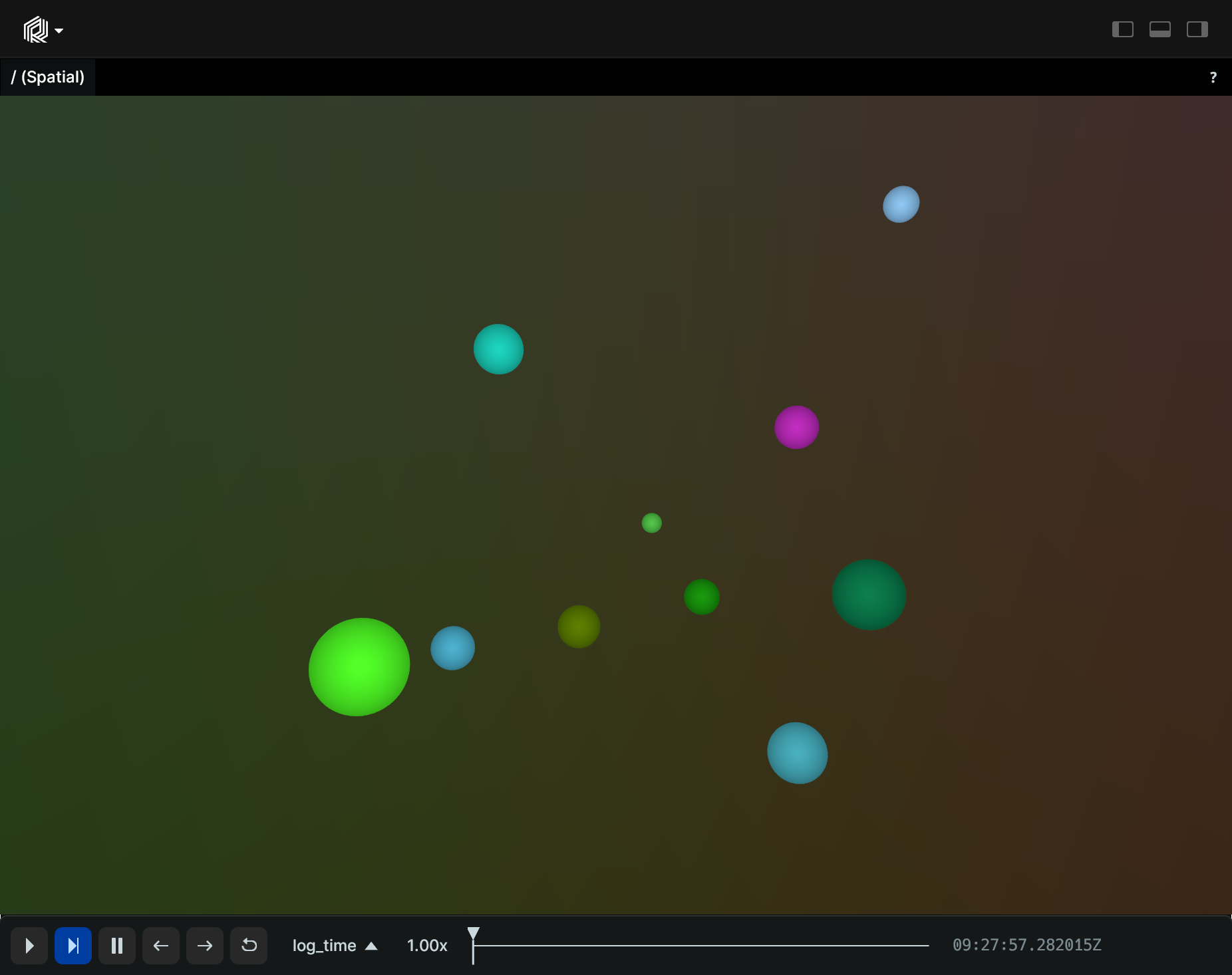
Randomly distributed 3D points with varying color and radius randomly-distributed-3d-points-with-varying-color-and-radius
"""Log some random points with color and radii."""
import rerun as rr
from numpy.random import default_rng
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d_random", spawn=True)
rng = default_rng(12345)
positions = rng.uniform(-5, 5, size=[10, 3])
colors = rng.uniform(0, 255, size=[10, 3])
radii = rng.uniform(0, 1, size=[10])
rr.log("random", rr.Points3D(positions, colors=colors, radii=radii))
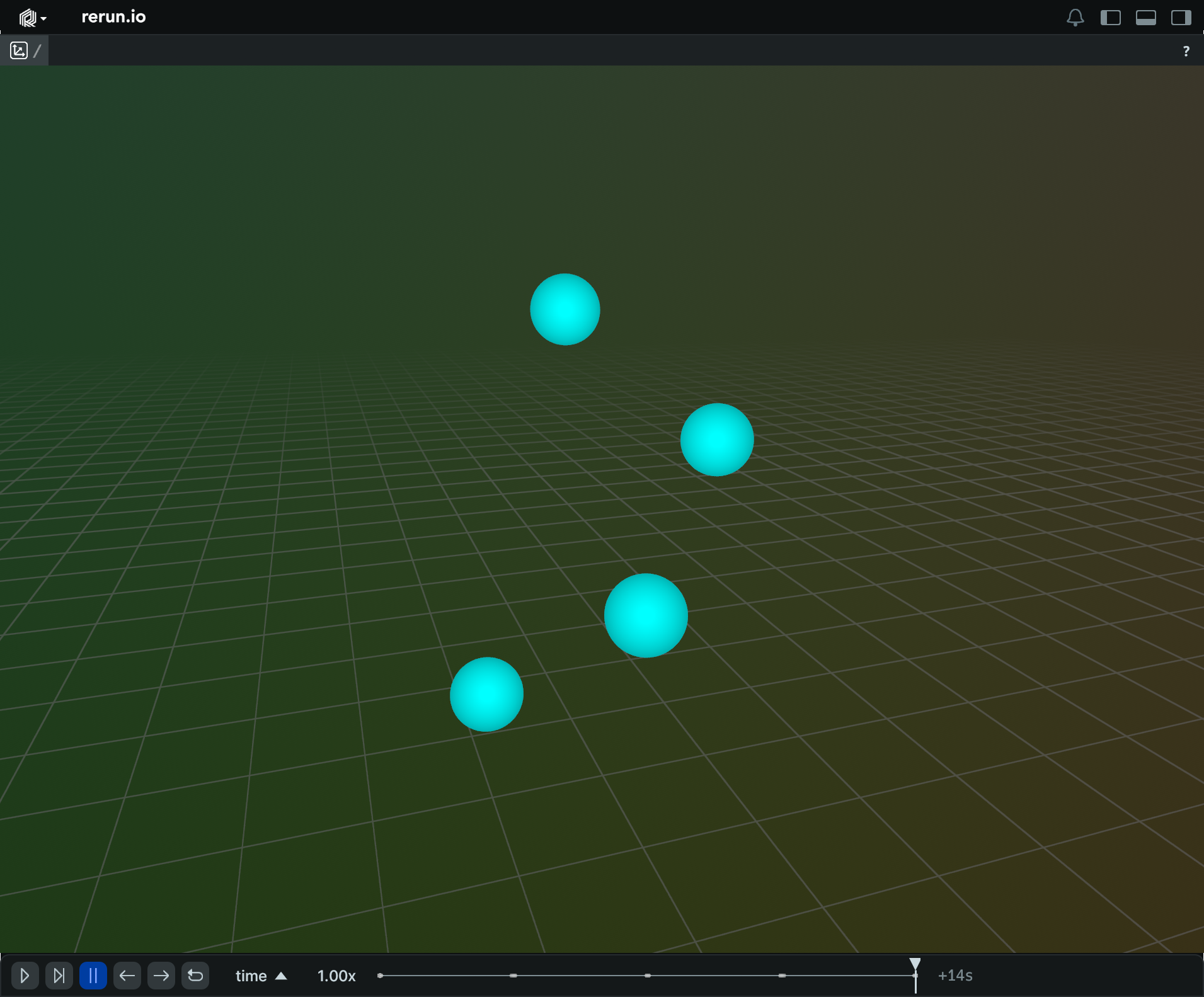
Log points with radii given in UI points log-points-with-radii-given-in-ui-points
"""Log some points with ui points & scene unit radii."""
import rerun as rr
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d_ui_radius", spawn=True)
# Two blue points with scene unit radii of 0.1 and 0.3.
rr.log(
"scene_units",
rr.Points3D(
[[0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]],
# By default, radii are interpreted as world-space units.
radii=[0.1, 0.3],
colors=[0, 0, 255],
),
)
# Two red points with ui point radii of 40 and 60.
# UI points are independent of zooming in Views, but are sensitive to the application UI scaling.
# For 100% ui scaling, UI points are equal to pixels.
rr.log(
"ui_points",
rr.Points3D(
[[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 1]],
# rr.Radius.ui_points produces radii that the viewer interprets as given in ui points.
radii=rr.Radius.ui_points([40.0, 60.0]),
colors=[255, 0, 0],
),
)
Update a point cloud over time update-a-point-cloud-over-time
"""
Update a point cloud over time.
See also the `points3d_column_updates` example, which achieves the same thing in a single operation.
"""
import numpy as np
import rerun as rr
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d_row_updates", spawn=True)
# Prepare a point cloud that evolves over 5 timesteps, changing the number of points in the process.
times = np.arange(10, 15, 1.0)
# fmt: off
positions = [
[[1.0, 0.0, 1.0], [0.5, 0.5, 2.0]],
[[1.5, -0.5, 1.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2.5], [-0.5, 1.5, 1.0], [-1.5, 0.0, 2.0]],
[[2.0, 0.0, 2.0], [1.5, -1.5, 3.0], [0.0, -2.0, 2.5], [1.0, -1.0, 3.5]],
[[-2.0, 0.0, 2.0], [-1.5, 1.5, 3.0], [-1.0, 1.0, 3.5]],
[[1.0, -1.0, 1.0], [2.0, -2.0, 2.0], [3.0, -1.0, 3.0], [2.0, 0.0, 4.0]],
]
# fmt: on
# At each timestep, all points in the cloud share the same but changing color and radius.
colors = [0xFF0000FF, 0x00FF00FF, 0x0000FFFF, 0xFFFF00FF, 0x00FFFFFF]
radii = [0.05, 0.01, 0.2, 0.1, 0.3]
for i in range(5):
rr.set_time("time", duration=10 + i)
rr.log("points", rr.Points3D(positions[i], colors=colors[i], radii=radii[i]))
Update a point cloud over time, in a single operation update-a-point-cloud-over-time-in-a-single-operation
"""
Update a point cloud over time, in a single operation.
This is semantically equivalent to the `points3d_row_updates` example, albeit much faster.
"""
from __future__ import annotations
import numpy as np
import rerun as rr
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d_column_updates", spawn=True)
# Prepare a point cloud that evolves over 5 timesteps, changing the number of points in the process.
times = np.arange(10, 15, 1.0)
# fmt: off
positions = [
[1.0, 0.0, 1.0], [0.5, 0.5, 2.0],
[1.5, -0.5, 1.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2.5], [-0.5, 1.5, 1.0], [-1.5, 0.0, 2.0],
[2.0, 0.0, 2.0], [1.5, -1.5, 3.0], [0.0, -2.0, 2.5], [1.0, -1.0, 3.5],
[-2.0, 0.0, 2.0], [-1.5, 1.5, 3.0], [-1.0, 1.0, 3.5],
[1.0, -1.0, 1.0], [2.0, -2.0, 2.0], [3.0, -1.0, 3.0], [2.0, 0.0, 4.0],
]
# fmt: on
# At each timestep, all points in the cloud share the same but changing color and radius.
colors = [0xFF0000FF, 0x00FF00FF, 0x0000FFFF, 0xFFFF00FF, 0x00FFFFFF]
radii = [0.05, 0.01, 0.2, 0.1, 0.3]
rr.send_columns(
"points",
indexes=[rr.TimeColumn("time", duration=times)],
columns=[
*rr.Points3D.columns(positions=positions).partition(lengths=[2, 4, 4, 3, 4]),
*rr.Points3D.columns(colors=colors, radii=radii),
],
)
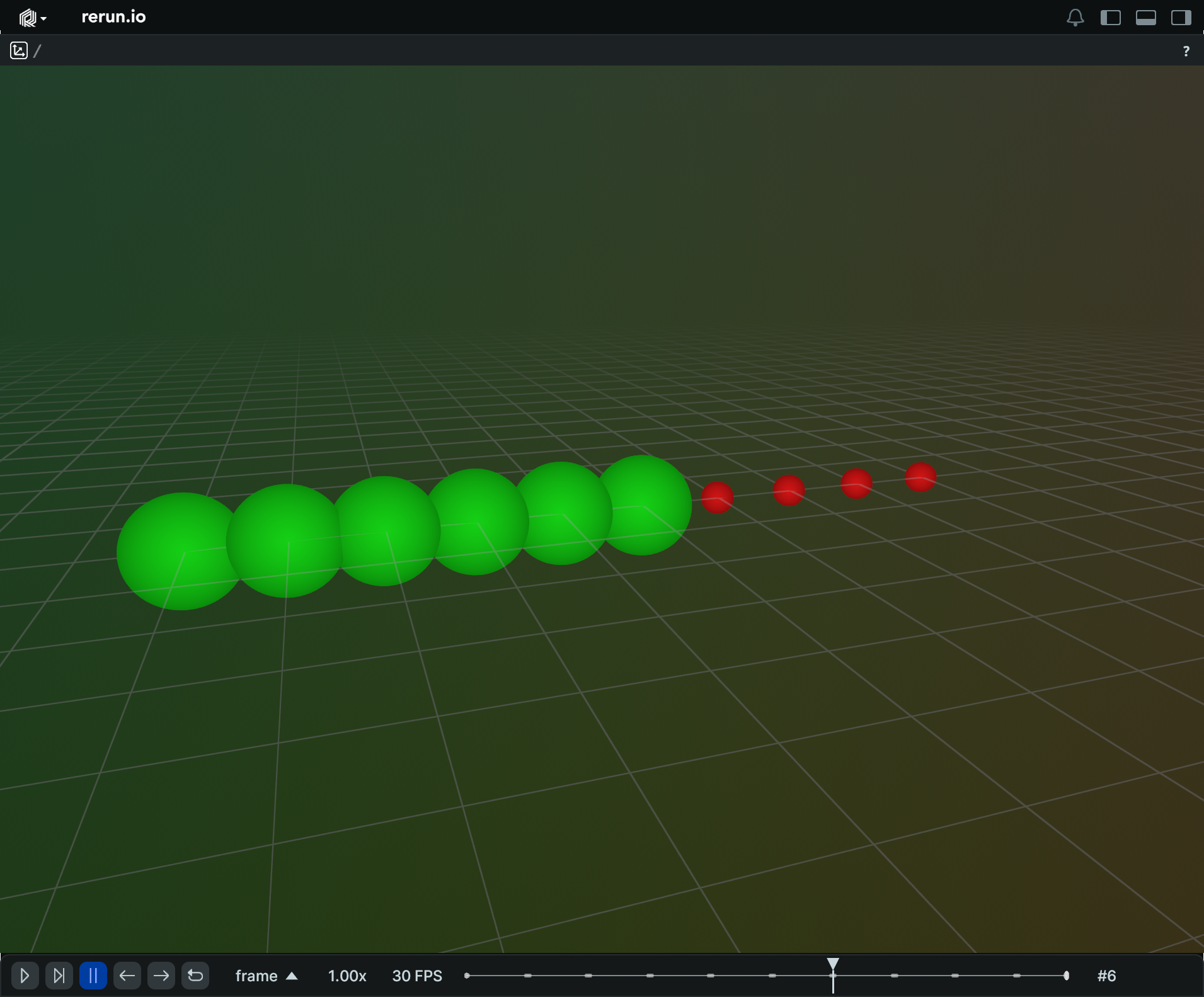
Update specific properties of a point cloud over time update-specific-properties-of-a-point-cloud-over-time
"""Update specific properties of a point cloud over time."""
import rerun as rr
rr.init("rerun_example_points3d_partial_updates", spawn=True)
positions = [[i, 0, 0] for i in range(10)]
rr.set_time("frame", sequence=0)
rr.log("points", rr.Points3D(positions))
for i in range(10):
colors = [[20, 200, 20] if n < i else [200, 20, 20] for n in range(10)]
radii = [0.6 if n < i else 0.2 for n in range(10)]
# Update only the colors and radii, leaving everything else as-is.
rr.set_time("frame", sequence=i)
rr.log("points", rr.Points3D.from_fields(radii=radii, colors=colors))
# Update the positions and radii, and clear everything else in the process.
rr.set_time("frame", sequence=20)
rr.log("points", rr.Points3D.from_fields(clear_unset=True, positions=positions, radii=0.3))