RRT*
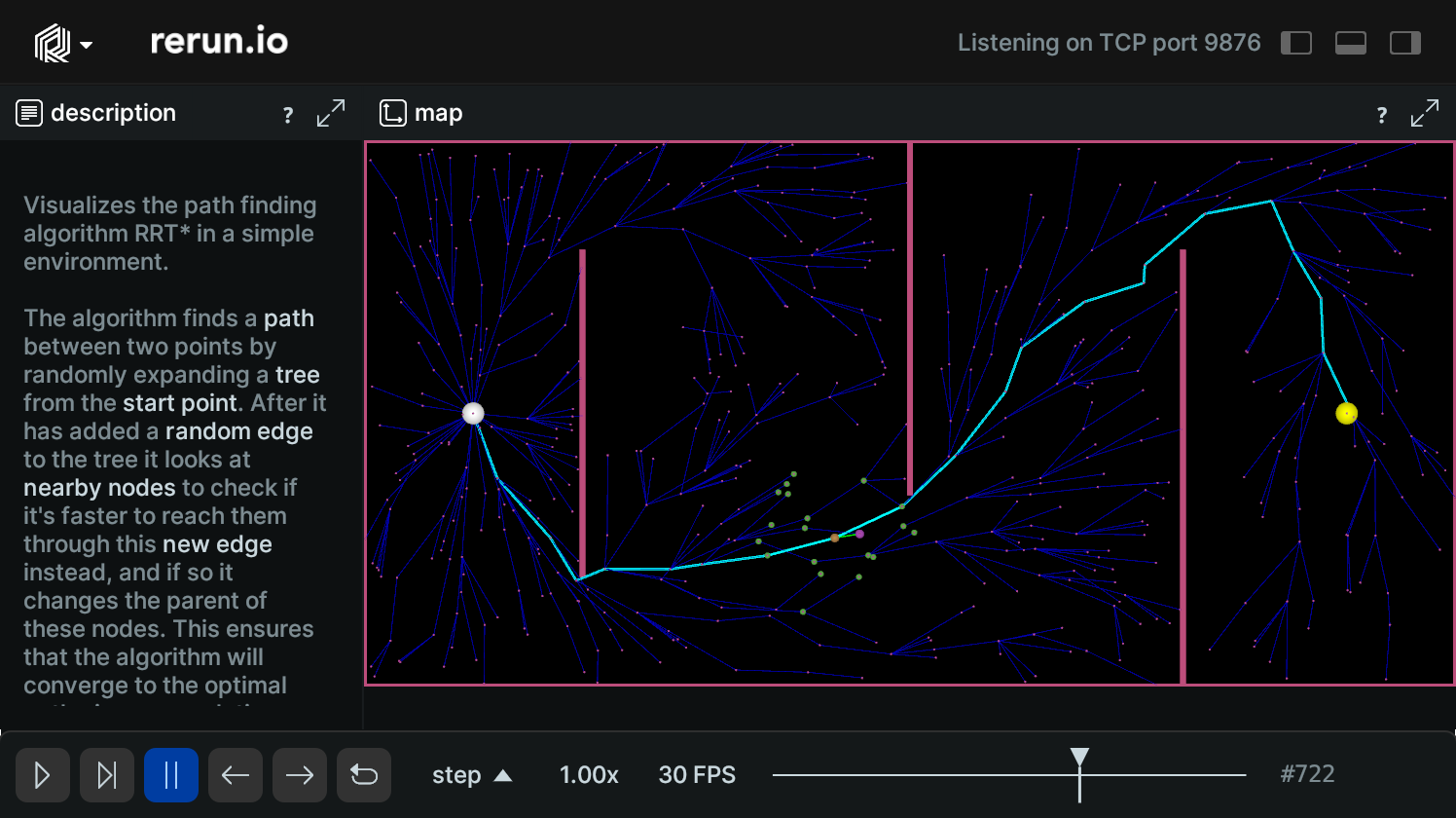
This example visualizes the path finding algorithm RRT* in a simple environment.
Used Rerun types used-rerun-types
LineStrips2D, Points2D, TextDocument
Background background
The algorithm finds a path between two points by randomly expanding a tree from the start point. After it has added a random edge to the tree it looks at nearby nodes to check if it's faster to reach them through this new edge instead, and if so it changes the parent of these nodes. This ensures that the algorithm will converge to the optimal path given enough time.
A detailed explanation can be found in the original paper Karaman, S. Frazzoli, S. 2011. "Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning". or in this medium article
Logging and visualizing with Rerun logging-and-visualizing-with-rerun
All points are logged using the Points2D archetype, while the lines are logged using the LineStrips2D LineStrips2D.
The visualizations in this example were created with the following Rerun code:
Map map
Starting point
rr.log("map/start", rr.Points2D([start_point], radii=0.02, colors=[[255, 255, 255, 255]]))Destination point
rr.log("map/destination", rr.Points2D([end_point], radii=0.02, colors=[[255, 255, 0, 255]]))Obstacles
rr.log("map/obstacles", rr.LineStrips2D(self.obstacles))RRT tree rrt-tree
Edges
rr.log("map/tree/edges", rr.LineStrips2D(tree.segments(), radii=0.0005, colors=[0, 0, 255, 128]))New edges
rr.log("map/new/new_edge", rr.LineStrips2D([(closest_node.pos, new_point)], colors=[color], radii=0.001))Vertices
rr.log("map/tree/vertices", rr.Points2D([node.pos for node in tree], radii=0.002), rr.AnyValues(cost=[float(node.cost) for node in tree]))Close nodes
rr.log("map/new/close_nodes", rr.Points2D([node.pos for node in close_nodes]))Closest node
rr.log("map/new/closest_node", rr.Points2D([closest_node.pos], radii=0.008))Random points
rr.log("map/new/random_point", rr.Points2D([random_point], radii=0.008))New points
rr.log("map/new/new_point", rr.Points2D([new_point], radii=0.008))Path
rr.log("map/path", rr.LineStrips2D(segments, radii=0.002, colors=[0, 255, 255, 255]))Run the code run-the-code
To run this example, make sure you have the Rerun repository checked out and the latest SDK installed:
pip install --upgrade rerun-sdk # install the latest Rerun SDK
git clone git@github.com:rerun-io/rerun.git # Clone the repository
cd rerun
git checkout latest # Check out the commit matching the latest SDK releaseInstall the necessary libraries specified in the requirements file:
pip install -e examples/python/rrt_starTo experiment with the provided example, simply execute the main Python script:
python -m rrt_star # run the exampleIf you wish to customize it, explore additional features, or save it use the CLI with the --help option for guidance:
python -m rrt_star --help