Notebook: minimal example
Overview overview
Rerun can be used directly within Jupyter notebooks. Many additional environments beyond Jupyter are supported such as Google Colab or VSCode.
You need the separate support package rerun-notebook to use this feature. Typically this is installed using:
pip install "rerun-sdk[notebook]"In order to show a Rerun Viewer inline within a notebook, you can call:
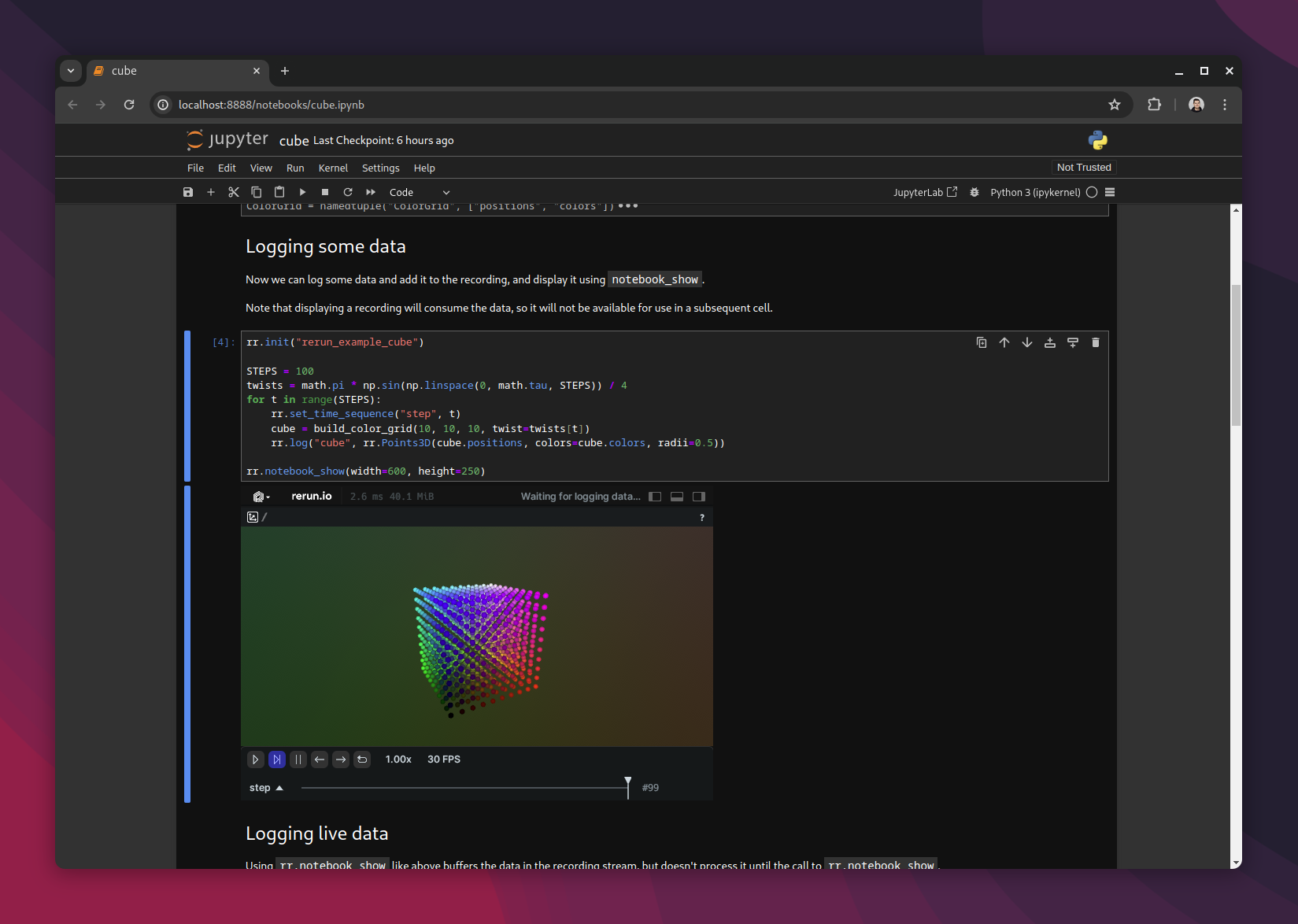
rr.init("rerun_example_notebook")
rr.log(...)
rr.notebook_show()This will show the contents of the current global recording stream. Note that the global stream will accumulate
data in-memory. You can reset the stream by calling rr.init again to establish a new global context.
As with the other stream viewing APIs (rr.show, rr.connect_grpc, rr.spawn), you can alternatively pass
a specific recording instance to notebook_show
rec = rr.RecordingStream("rerun_example_notebook_local")
rec.log(...)
rec.notebook_show()Running in Jupyter running-in-jupyter
The easiest way to get a feel for working with notebooks is to use it.
First, install the requirements (this includes Jupyter, the Rerun SDK, and the notebook support package)
pip install -r requirements.txtThen, open the notebook
jupyter notebook cube.ipynbFollow along in the browser that opens.